Three Worlds of Welfare Capitalism
What is Political Economy?
The study of how politics affects economic outcomes and, vice-versa, how economics affects political outcomes.
The OECD
The Welfare State
A system through which the government provides for the most basic needs of its citizens.
Examples?
Other Key Terms
- Social policy–The range of policies that governments use to promote welfare
- Social contract–Implicit agreement to give up individual rights in exchange for social rights
- Social rights–Rights to basic services like education, health care and a minimal standard of living
- Decommodification–The ability of a person to opt out of working
- Universalism–Benefits provided in such a way that everyone has an equal ability to access them
Welfare State Regimes (“Three Worlds”)
- Liberal—emphasize means tested social assistance
- Anglo-American countries (e.g. U.S., UK, Australia)
- Corporatist—ranked system of social insurance
- Continental European countries (e.g. Austria, Germany, Switzerland)
- Social Democratic—universalistic, emphasis on full employment and broad provisioning - Nordic countries (e.g. Denmark, Norway, Sweden)
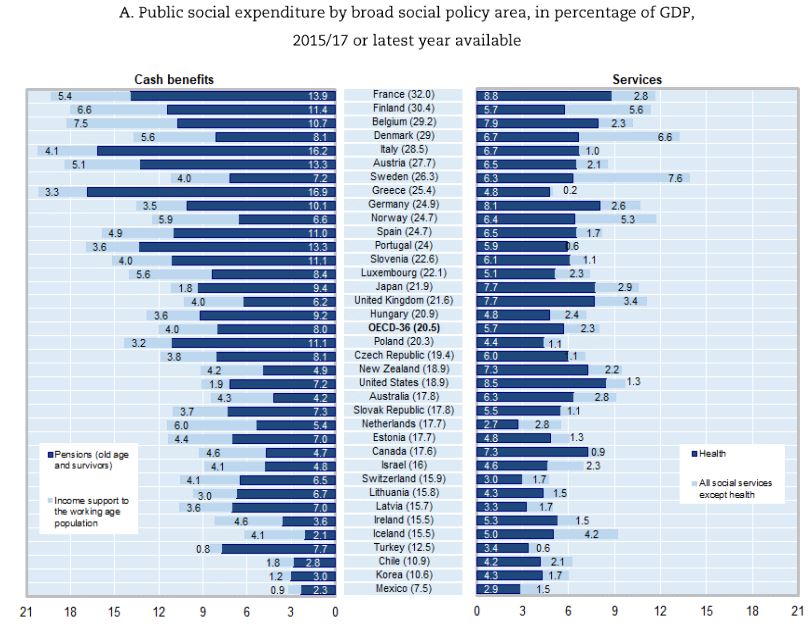
Social Spending By Category
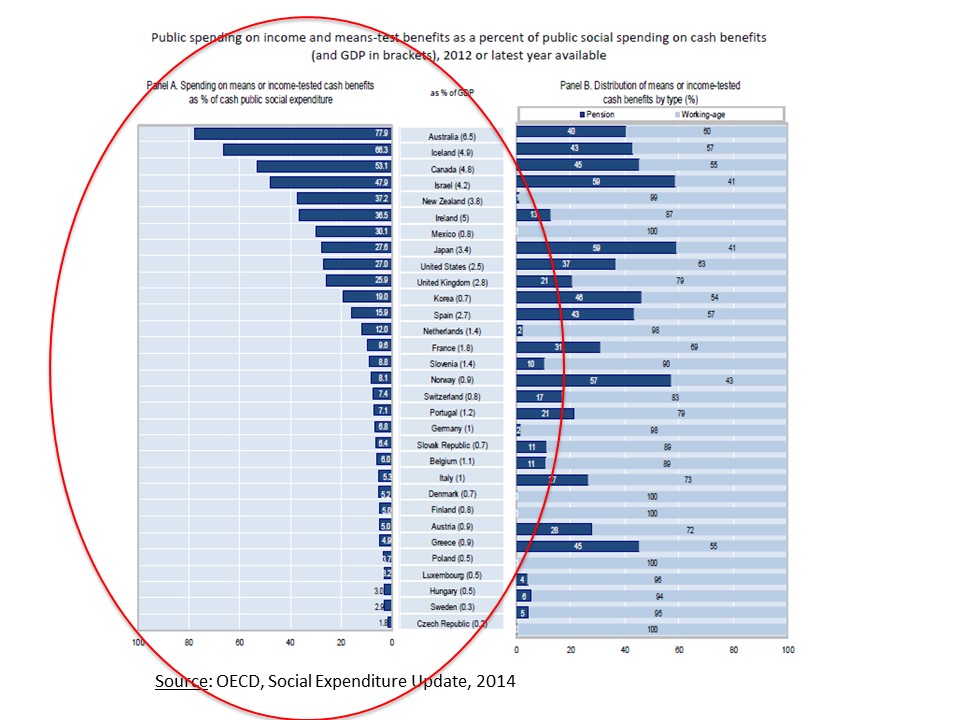
Means Tested Benefits
Pillars of Social Democracy
-
Swedish Prime Minister Stefan Löfven video
-
Three pillars of the Nordic model
- Full Employment
- Universal and Generous Welfare System
- Organized Labor Market
-
Think about
- How each pillar is important
- How they work together to support the system
Retrenchment and Convergence
- Race to the bottom hypothesis
- Globalization induces states to drastically reduce publicly provided benefits and services
- Embedded liberalism hypothesis
- Globalization induces states to spend more on benefits and services to cushion workers from increased labor market risks
- Convergence
- Globalization forces states to provide similar levels and types of benefits and services
Education Spending in Three Worlds
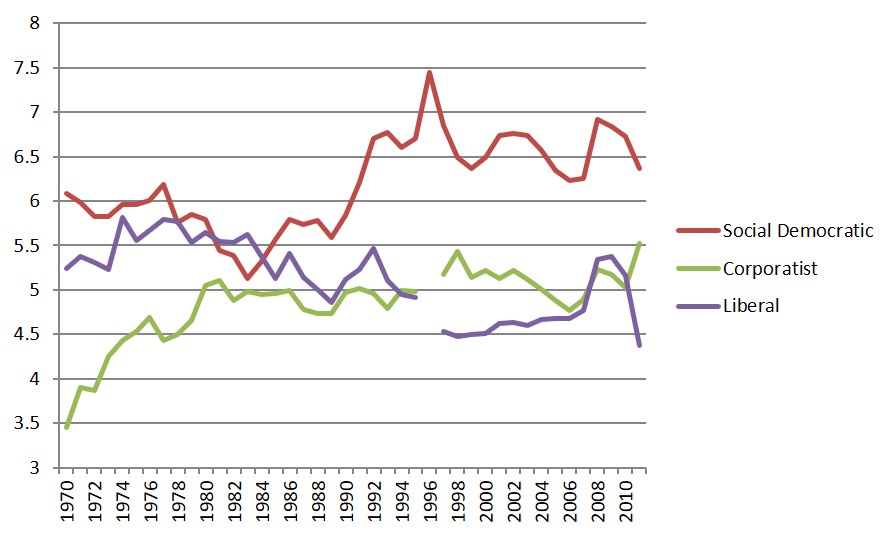
Health Spending in Three Worlds
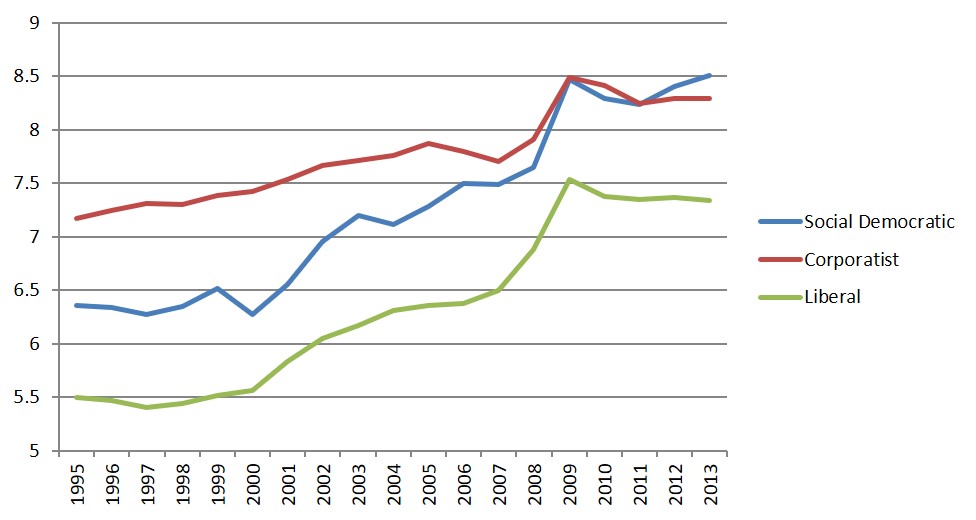
Reasons for Persistence
- Trade openness—induces countries to spend more to cushion workers (embedded liberalism)
- Partisan politics—Christian democratic and social Democratic parties favor welfare state (but different kinds)
- Electoral politics (voters like programs)
- Bureaucratic inertia (vested interests)
- Economic coordination (next section)
Discussion
-
Why do some countries have higher levels of redistribution?
- Iversen and Soskice
-
Bernie Sanders Loves Denmark video
-
Can “democratic socialism” work in the United States
- Is it the American dream “for real”?
- Is it possible in a U.S. context