Women in Politics
-
How does women’s representation vary cross-nationally and over time?
-
Why is women’s representation important?
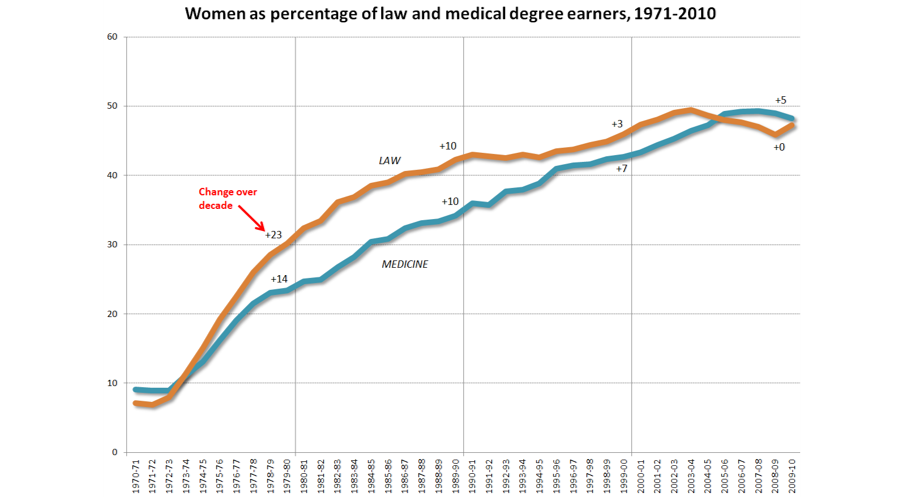
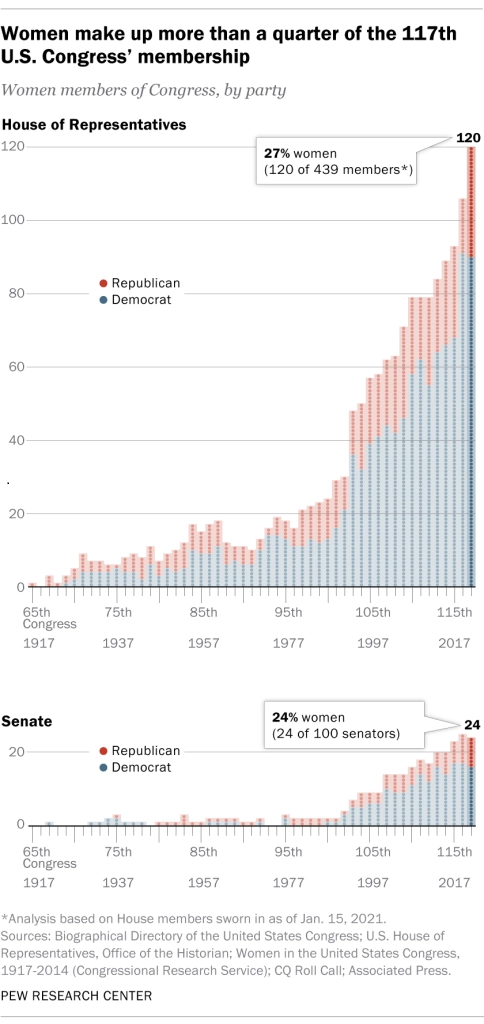
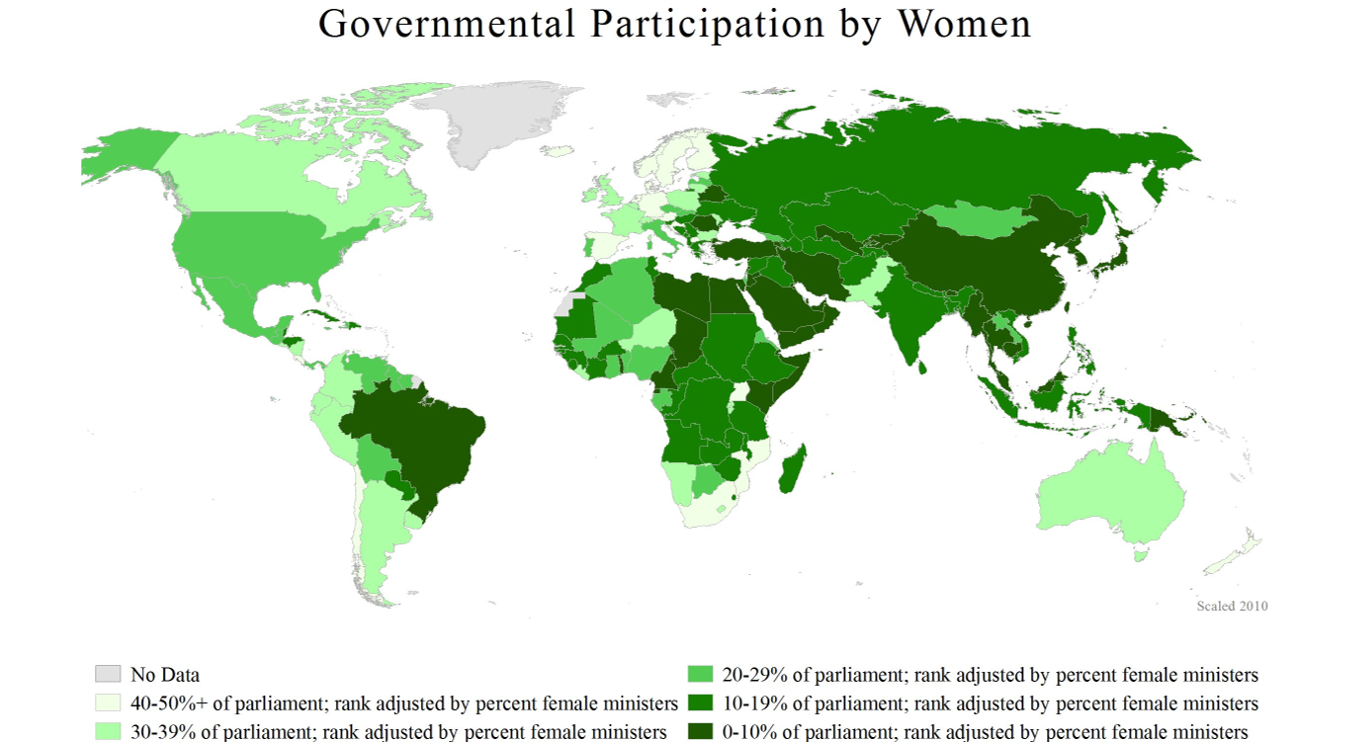
Seats Held by Women
- Rwanda (61.3%)
- New Zealand (48.3%)
- Mexico (48.2%)
- Nicaragua (47.3%)
- Sweden (46%)
- Denmark (39.7%)
- Italy (35.7%)
- Canada (29.6%)
- United States (27.2%)
- Japan (9.9%)
Based on data from iup.org
Regional Averages
- Americas (32%)
- Europe (30.6%)
- Sub-Saharan Africa (25.1%)
- Asia (20.8%)
- MENA (19.3%)
- Pacific (18%)
Explanations
-
Economic Factors
-
Institutional Factors
-
Cultural Factors
Economic Factors
-
Developing Countries
- Female literacy
- Fertility rates
- Employment
-
Advanced Industrial Democracies
- Maternity leave
- Access to daycare
- Scheduling flexibility
Institutional Factors
-
Electoral systems
- PR vs SMD
-
Level of democratization
- Respect for human rights
- Party competition
-
Gender quotas
Gender Quotas
-
Type
- Voluntary party quotas
- Candidate quotas
- Reserved seats
-
Effectiveness: one study found quotas increased women’s representation by 9%
Cultural Factors
-
Political socialization: how people are taught by society to think of their roles in public and private spheres
-
Socialization influences
- Whether women come forward
- How they are viewed by party leaders
- How women are viewed by voters
Preferences
-
Desire to be at home
-
Family obligations increase cost of entry
-
Aversion to conflict
History
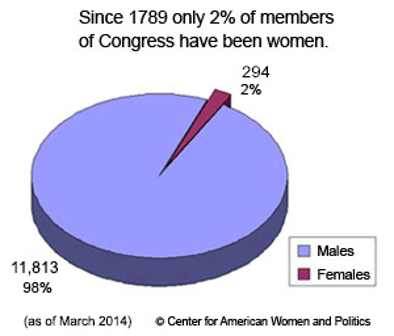
How Women are Viewed
-
Taste Discrimination
- Voter preference for male candidates
-
Statistical Discrimination
- Not enough examples of female leaders
-
Recent Study
- “Men make better political leaders”
- Gender discrimination is “sticky”
- More prevalent in non-egalitarian cultures
Discussion
-
With reference to Krook and Norris, what is the most compelling explanation for variations in women’s representation? What is the best way forward in terms of boosting women’s representation?
-
With reference to Waylen, why is politics dominated by men in most countries? How does her explanation differ from that of Krook and Norris?
-
Which explanation/framework is more compelling?